In the second chapter of Information Technology In Business we will learn about the competitive advantage and the subunit that we will learn in it that is Porter's Five Forces Model, Porter's 3 generic strategies and the relationship between business process and value chain.
What is mean by competitive advantage?
Basically competitive advantage mean a product or service that an organization's
customers place a greater value on than similar offerings from a competitor. Even thought, it give an organization's customers place a greater value on than similar offerings from a competitor but competitive advantage only temporary because the competitors keep duplicate the strategy. That will make the company to start a new competitive advantage.
- Michael Porter's Five Forces Model.
A useful tool to aid organization in challenging decision whether to join a new industry or industry segment. Under Porter's Five Forces Model there are five model that we need to know that is :
- Buyer Power
- Low = When their choices are few.
In order to reduce buyer power and create a competitive advantage, an organization must make it to be more attractive in order to attract customer to buy from them and not from their competitors.
The best practices of IT- based is through the loyalty program in travel industry. As an example a reward on free airline tickets or hotel stays.
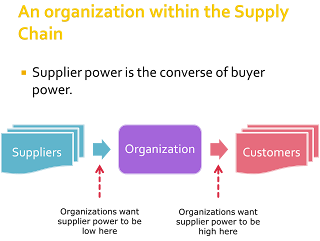
- Supplier Power
- Low = when their choices are many.
The best practices IT to create a competitive advantage is :
- B2B Marketplace = a private exchange allow a single buyer to posts it needs and then open the bidding to any supplier who would care to bid.
- Reverse Auction = an auction format in which increasingly lower bids will win.
- Threat of Substitute Products and Services
- Low = when there are a few alternatives from which to choose.
Usually, an organization would like to be on a market in which there are a few substitutes of their product or services. As an example is an electronic product that has the same function but they come from different brands. In order to overcome this obstacles is by implementing the switching cost that is a costs that can make the customer to feel reluctant to switch to another product or service.
- Threat of New Entrants
- Low = when there are significant entry barrier ( a product or service feature that the customers have come to expect from an organization and it must be offered by entering organization in order to compete and survive ) to entering a market. As an example a new bank must offers online paying bills, account monitoring in order to compete with the other existing bank.
- Rivalry among existence competitors
- Low = when competition is more com placement
Existing competitors are not much of the threat as each of them has found their "niche". However , if there is changes in management,ownership, or " the rules of the game " it can give a serious threat to long term survival from existing firms.
- Example : the airline industry faces serious threat from airlines operating in bankruptcy, who do not pay on the debts while slashing fares against those healthy airlines who do pay on debt.
2. Porter's 3 generic strategies
- Cost Leadership.
- Competitors with higher costs cannot afford to compete with the low-cost leader on price.
- Differentiation
- Unique features or benefits may justify price differences and/ or stimulate demand.
- Example : i-care by Proton.
- Focused Strategy
- Concentrates on either cost leadership or differentiation.
3. Relationship Between Business Process and Value Chain
- Supply Chain - A chain or series of processes that adds value to product and service for customer






0 comments:
Post a Comment